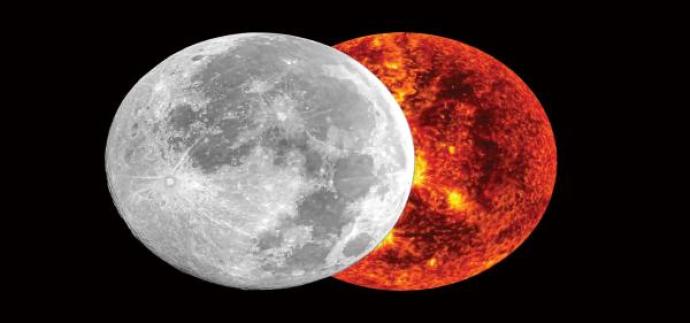
A solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun. The Moon stops the Sun’s light from reaching the Earth. This casts a shadow of the Moon onto the Earth.
There are different kinds of solar eclipse. During a total eclipse, the Moon completely blocks the Sun; the only light left is a glow from the Sun's outer layer. This does not happen often because the Sun, Moon and Earth all need to be in a perfect line. During a partial eclipse, the Moon only blocks part of the Sun. The Sun appears to have a dark shadow on only a small part of its surface. These types of eclipses occur more often.
Even though the Moon is much smaller than the Sun, it is much closer to the Earth. This is why the Moon and Sun appear to be the same size in the sky.
Have a go at this simple paper-based activity and create the different phases of a total solar eclipse!
By the end of this resource you will:
- Be able to explain what a solar eclipse is.
- Have made and used a model of a solar eclipse.
- Have observed how the shape of the Sun changes during a solar eclipse.
To complete this resource you will need:
- A printed copy of the worksheet (below)
- Scissors.
- To watch the What Happens During a Solar Eclipse? animation. This will help you identify each stage of the eclipse.
- The answers to the worksheet (below) to check your work at the end.