Star Formation
Stars form in huge clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. These areas of space are sometimes known as 'stellar nurseries' or 'star forming regions'.

Stellar Evolution
All stars form in nebulae, huge clouds of gas and dust.
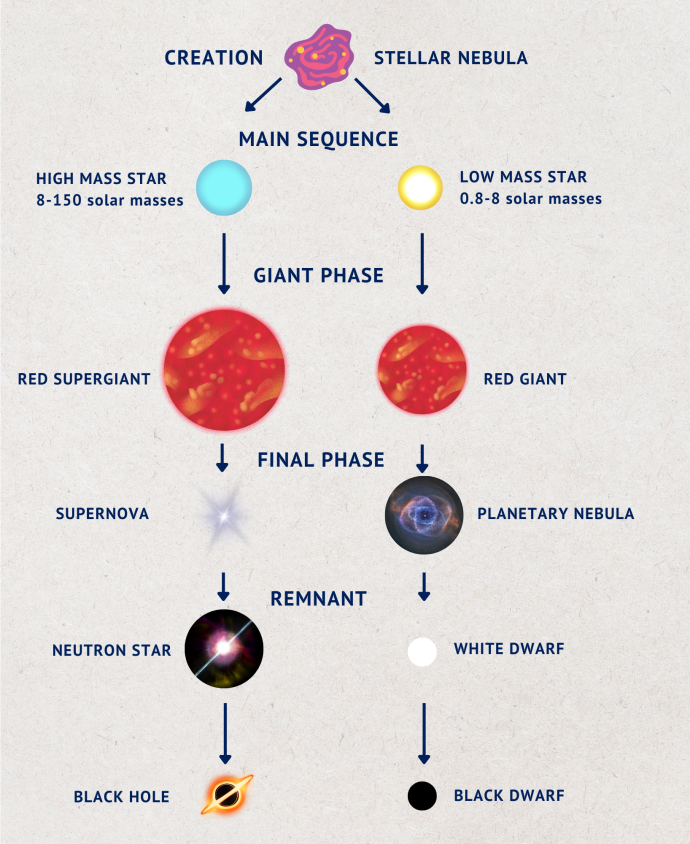
Though they shine for thousands of years, stars do not last forever. The changes that occur in a star over time and the final stage of its life depends on a star's size.
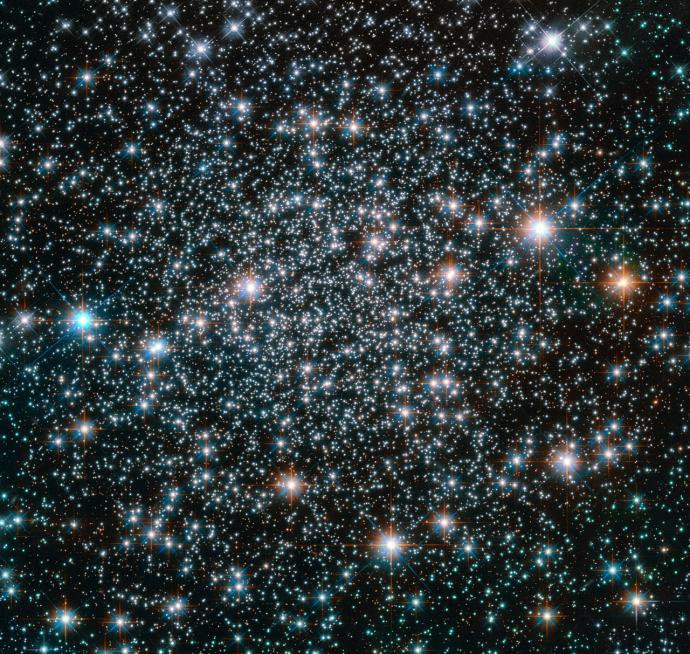
Star Clusters
Star clusters are groups of stars which are held together by gravity.
There are two types of star clusters: globular clusters and open clusters.
Stellar Classification
Astronomers began to categorise stars, based on their mass and temperature, hundreds of years ago. As scientists have learned more about stars, this classification scheme has had to evolve.

Stars
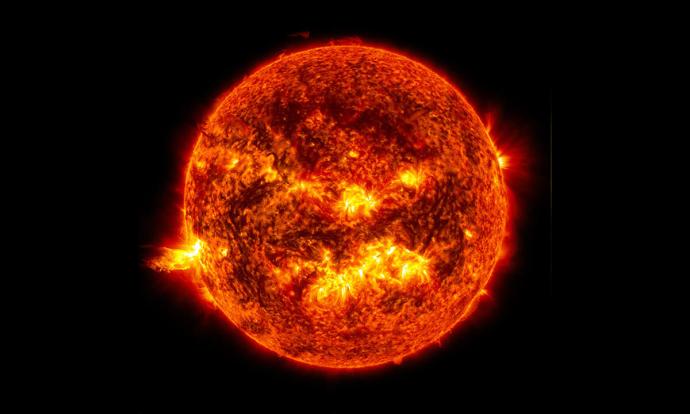
Stars are massive, glowing balls of extremely hot gas (called plasma) in space. The Sun is our closest star.
Brightness
Light is the main signal we receive from space. Almost everything we know about space has been found by measuring light.
One of the main ways to measure light is to look at the brightness. Measuring the brightness of something in space isn't as easy as you'd think though.

Nuclear Physics
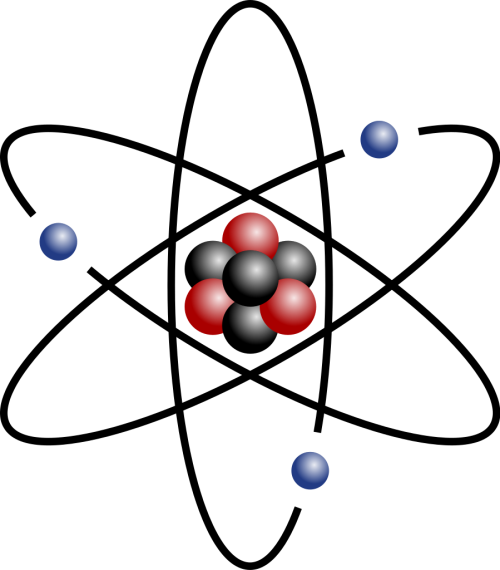
Nuclear physics is the branch of science which looks inside atoms. It looks at the nucleus, and what effect different interactions have on it.
Understanding our Universe
The universe has always amazed people. Over time, our understanding of stars and galaxies has changed a lot.

Claudius Ptolemy
Occupation
Mathematician, Astronomer, Geographer
Year born
100 AD
Research Areas
Movements of planets and stars, Cartography

