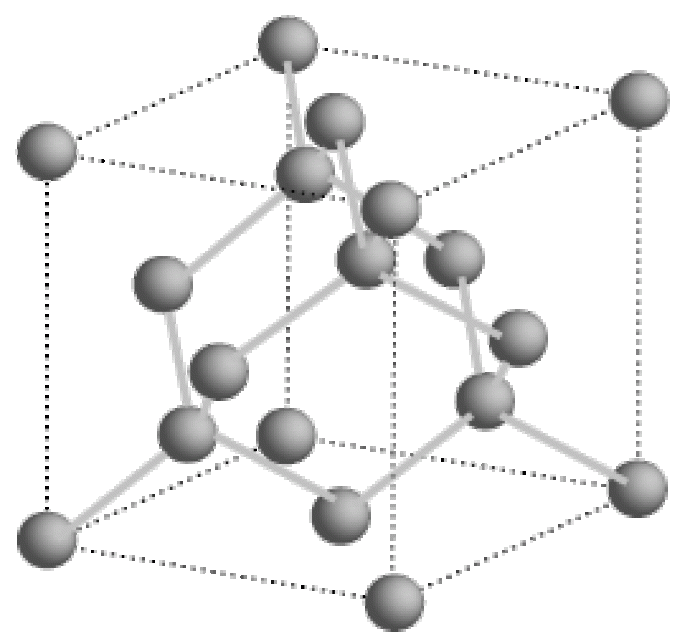
Semiconductors
Semiconductors are an important part of CCD cameras (Charge-coupled Devices). They help to convert light into a current in the technology.
Electricity
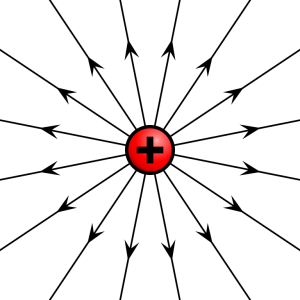
Some particles can have a positive or negative charge. For example, protons have a positive charge, and electrons have a negative charge.
They have electric fields around them. The stronger the charge, the bigger the electric field.
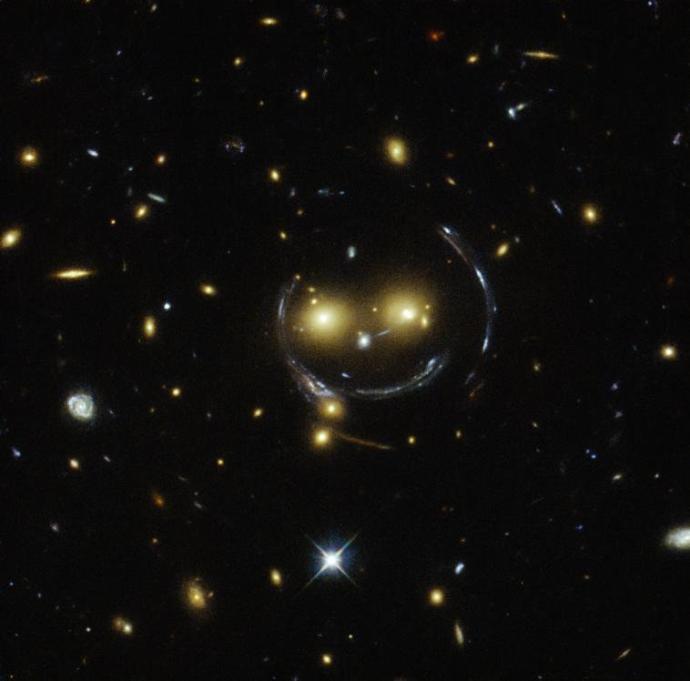
Gravitational Lensing
Space is not flat. It is 3D, and we say that everything in it is held together on an imaginary surface we call spacetime. The idea of spacetime was put forward in Einstein's theory of relativity.

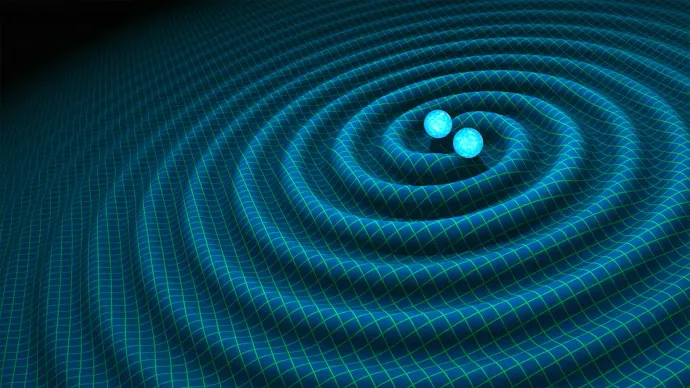
Gravitational Waves
Gravitational waves are tiny, invisible ripples in space. They travel for huge distances at the speed of light. The waves squeeze and stretch any objects they pass, but only by a tiny amount.
Relativity
Gravity is the force we are most familiar with in everyday life. It has been studied for longer than the other forces of nature. However, it is also the least well understood.

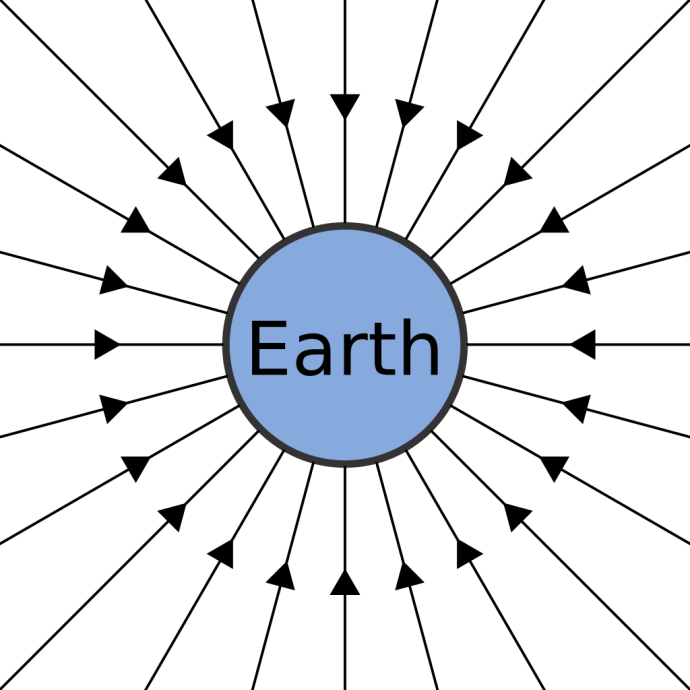
Gravity
Gravity is the name of the force that pulls objects together. It is a non-contact force. This means it acts on objects that are not touching each other.

Light and Telescopes
One of the first people to study light was Ibn al-Haytham (known as Alhazen). He was a Muslim, living in Egypt in the early 11th Century. Alhazen is first person we know of who used the scientific method. He wanted to know why our eyes could see things.
Isaac Newton
Occupation
Mathematician, Astronomer, and Physicist
Year born
1643
Research Areas
Optics, maths, motion, gravity

